Language of evaluation
1,2. (3.5 pts each) We wish to test the model that red cars have at least 1.5 times higher accident rates (per car per mile) than white cars. For the following possible data, which consequences (A-D) apply? Note that this question is not about causation versus correlation, only about data and a model that happens to describe a correlation. Answer each question independently of the others. At least one answer, but possibly more (MTF). Ignore the possibility of sampling error.
|
A) The data are inconsistent with the model |
B) The data are consistent with the model |
C) The data support the model |
D) The data are irrelevant to the model |
E) None |
1) Data: Accident rates by color of car per 10,000 miles:
white = 1%, blue = 0.6% tan = 0.7% green = 0.4%, red = 1.5%. A B C D E
2) Data: Accident rates by color of car per 10,000 miles:
white = 1%, blue = 0.6% tan = 0.7% green = 0.4%, red = 2%. A B C D E
Correlations & Causation
3. (8 pts) Which of the following statements describe a (non-zero) correlation? Do not choose any option that describes a zero correlation or for which a correlation is undefined. If insufficient information is given to determine whether a correlation exists, treat it as if there is no correlation. MTF
(A) More people attend the Kerrville Folk Music Festival than attend the Rice Festival.
(B) Two thirds of UT students voted in student government elections; one third did not vote.
(C) Global average yearly temperatures have been increasing over the last few decades
(D) More people buy products endorsed by Michael Jordan than products endorsed by O.J. Simpson
(E) The world’s population has doubled in the last 60 years.
(F) Customer sales at Austin Restaurant Supply have been flat (unchanged) over the last 7 years.
(G) Retail sales in the U.S. are higher in December than in any other month.
(H) Death rates for skydiving are 1 in 100,000 jumps; death rates for driving are about 1 in 170,000 miles driven.
4. (5pts) Key code, name, and ID number. Fill in (A B) in scantron field 4 to indicate your key for this version of the exam.
Be sure your name and personal ID number are correctly bubbled in on the scantron.
Your name is required on this exam form and the scantron form to receive credit for this test.
5. (7 pts) Wording has changed!!! Mark all models(s) that are inconsistent with the information in the following graph. That is, mark an answer if it CAN be ruled out using the information in the following graph. Assume you have no data other than what is presented in this graph. MTF
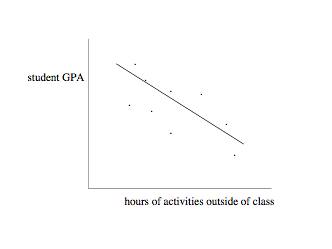
(A) Student GPA is correlated with hours of activity outside of class
(B) Student GPA is negatively correlated with hours of activity outside of class
(C) Student GPA is positively correlated with hours of activity outside of class
(D) Getting a high GPA motivates a student to give up activities outside of class
(E) Getting a high GPA motivates a student to take up activities outside of class
(F) Taking up activities outside of class competes with study time and lowers a student’s GPA
(G) Taking up activities outside of class increases a student’s GPA
(H) Fluoride causes changes in tooth decay.
6) (4pts) Consider a correlation between variable Y and diabetes. If X (not Y) is the factor that affects diabetes rate, which diabetes rates are expected in cells 1 & 2 of the following table? Assume that no other variables besides X and Y are important. (one answer only)
|
|
|
Y: |
|
|
|
|
absent |
present |
|
X: |
absent |
(1) |
low diabetes |
|
present |
high diabetes |
(2) |
|
|
A) 1 is high, 2 is high |
C) 1 is low, 2 is high |
|
B) 1 is high, 2 is low |
D) 1 is low, 2 is low |
7. (6 points) Which of the following constitutes an example of inferring causation from correlation (i.e., in which a correlation leads someone to infer the causal basis of the correlation)? Base your answer only on the information provided. Do not circle answers that merely describe a correlation, that infer correlation from causation, or that test the causal basis of a correlation. MTF
(A) The Centers for Disease Control observes that countries with a high content of fish in the diet have lower heart disease rates than countries with low fish content in the diet. They then divide 1,000 U.S. citizen volunteers into one group that is fed 1 pound of fish/week and another group that is fed only 1 pound of fish/month.
(B) Quitting the smoking habit reduces a person’s lung cancer rate. As a consequence, former smokers who have quit the habit have lower lung cancer rates than those who continue smoking.
(C) People who drink modest amounts of alcohol have higher survival rates than people who drink nothing and than people who drink excessively. As a consequence, the medical profession is now beginning to suggest that modest alcohol consumption is a way to enhance longevity.
(D) The global average temperature has increased over the last 50 or so years, following increased output of so-called greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane) produced by human activities. Anti-environmentalists argue that the global warming is independent of and has nothing to do with human activities.
8. (6 pts) Consider the correlation that:
people in cities and towns with high fluoride in the water have low tooth decay rates
Which of the following causal models of this correlation use a “third variable” to explain the correlation? Use the method given in class to distinguish whether a 3rd variable is invoked. Do not mark an option if the correlation goes in the wrong direction (e.g., that cities of high fluoride have higher levels of decay). MTF
Causal model |
Cause invoke a third variable? |
|
water with high fluoride also has high magnesium, and high magnesium reduces tooth decay |
Fill in (A) if a 3rd variable is invoked |
|
high fluoride inhibits the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay, and it is the lower levels of bacteria in water with high fluoride that result in lower tooth decay rates |
Fill in (B) if a 3rd variable is invoked |
|
water with high fluoride comes from sources that also have fewer bacteria that cause tooth decay, and it is the lower levels of bacteria that result in lower tooth decay rates |
Fill in (C) if a 3rd variable is invoked |
|
high fluoride makes teeth resistant to tooth decay by affecting the properties of enamel |
Fill in (D) if a 3rd variable is invoked |
9-11. (3.5 points each) Gotham City has a long history of upholding high moral standards, and its residents have consistently voted for high beer taxes. Mayberry residents like beer and have consistently voted to keep beer taxes low. Researchers have discovered that Gotham City has high STD rates in teenagers, whereas Mayberry has low teen STD rates. Residents of Gotham City have thus proposed lowering beer taxes as a way of reducing STD rates.
Use the following variables:
Variable 1: STD rate
Variable 2: beer tax rate
Variable 3: city
For each of the following questions, you are given a pair of these variables. You are asked to choose among the following 3 options that best characterizes their relationship in the problem description above.
|
(A) no correlation or causation is indicated. |
(B) a correlation is indicated, but no causation between the variables is suggested |
(C) a correlation is indicated & a causal relation between the variables is suggested or described |
For each pair of variables given below, which option applies (one answer each)?
9. Variables 1 & 2: (A) (B) (C)
10. Variables 1 & 3: (A) (B) (C)
11.Variables 2 & 3: (A) (B) (C)
Controls
12. (5 pts) The Monty Python video on penguin intelligence compared the performance of humans and penguins on an IQ exam. Consider the last test shown in that video (with the immigrants at the zoo). Mark all of the following factors that were controlled for in that IQ test shown (recall that a factor controlled for is one that is matched across the different groups being compared).
|
(A) inability to speak English |
(D) body size |
|
(B) ability to speak English |
(E) testing environment |
|
(C) brain size |
(F) environment in which the subjects were born and raised |
13,14. As described in the Book, epidemiologists in Britain noted a correlation that certain cancers were more frequent among residents living near nuclear power plants than in the population at large. The following two questions pertain to this study and its implications.
13. (4pts) Which of the following models are consistent with this correlation? MTF
(A) nuclear power plant locations reduce cancer rates, but the people who live in these locations have ethnic cultures that elevate their cancer rates
(B) nuclear power plant locations have no effect on cancer rates, but the people who live in these locations have ethnic cultures that elevate their cancer rates
(C) nuclear power plant locations increase cancer rates
14. (4pts). Now suppose that we had been randomly assigning where people live in Britain over the last 100 years, and that we still observed that residents living near nuclear power plants had higher-than-average cancer rates. (Randomly assigning where a person lives would of course be unethical. However, assume for the sake of this question that it could be done.) Which of the following models would now be consistent with this correlation? MTF
(A) nuclear power plant locations reduce cancer rates, but the people who live in these locations have ethnic cultures that elevate their cancer rates
(B) nuclear power plant locations have no effect on cancer rates, but the people who live in these locations have ethnic cultures that elevate their cancer rates
(C) nuclear power plant locations increase cancer rates
15. (5 pts) Each of rows (A)-(G) describe different treatments that could be applied to cornfields in attempting to maximize yield. The treatments differ in which factors are present (indicated by “+”) or absent (-). Factor 1 is fertilizer; factor 2 is insecticide; factor 3 is herbicide; factor 4 is plowing before planting; factor 5 is use of genetically modified seeds. For each treatment, the data gathered are the pounds of corn harvested per acre.
Which two treatments would you want to compare to determine if factor 1 is correlated with differences in corn harvested when all other factors are controlled? In evaluating possible answers, pick any comparison that controls for all unwanted factors, and assume that these treatments differ only in the ways stated. Mark exactly two options, or option I if none apply. Each row (each option) describes a different set of conditions, so to know which factors would be applied in a treatment, you look across the row. If multiple combinations satisfy the problem, any correct combination will be accepted. (Two answers or None; options have changed).
|
|
factor |
|||||
|
Option |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
(A) |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
|
|
(B) |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
|
|
(C) |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
+ |
|
|
(D) |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
|
|
(E) |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
(F) |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
|
|
(G) |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
+ |
|
|
(H) |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
|
|
(I) |
No combination satisfies the request |
|||||
16. (5 pts) Control groups versus controlled factors. A professor conducts an experiment to determine how students can improve their exam scores. She uses two Sections of the same course that she teaches (each with different students) and lets the students in one section go about their business as usual (= the control group). For the other section (the treatment group), she dictates the students’ sleeping, eating, and studying habits for a week. She then gives the same exam to both sections at their usual times and compares the scores between 50 randomly chosen male students of one section to the scores of 50 randomly chosen males from the other section. What factors are explicitly controlled for (matched) in the design of this study? Do not infer more than is given. MTF
|
(A) Section |
(D) student sleeping habit |
|
(B) student gender |
(E) time and day of exam administration |
|
(C) student eating habit |
(F) prior exam performance of the student |
Experiments
17. (5pts) Which options about the in-class personality survey are true? MTF
(A) It was an experiment because the survey used a blind design.
(B) Most of the Bio301 students scored the personality description of themselves as reasonably accurate (a score of 3 or better in a range of –5 to +5).
(C) A video shown in class performed an experiment with a mock horoscope that had several features in common with the Bio301 experiment.
(D) The personality descriptions in these experiments (our class and the video) were specific in many details about the person.
(E) The study shown in the video (and used in class) would have been improved by including a group in which the personality description was assigned randomly to the student.
18. (6pts) Prisoners of Silence video. Which of the following options about the FC (facilitated communication) video are true? MTF
(A) Experiment: Lecture and the book described two types of experiments regarding how to control for unwanted correlations among variables. The FC experiment was the type in which unknown hidden variables were controlled for by randomization.
(B) Replication: tests were conducted with multiple autistic children, multiple facilitators, and the type of test was even varied.
(C) Controls: in these studies, the controls were the parts of the tests in which the facilitator and child were shown the same information.
(D) Blind was an essential feature of these tests.
19. (7 pts). Which of the following studies describe experiments, regardless of whether the experiment was designed well or poorly and regardless of ethics. In each problem, the goal is given. The question is whether the option describes an experiment with respect to the goal. MTF
(A) To test whether smoking causes lung cancer, you interview people about their smoking habits. You then take the smokers and pay a randomly-chosen half of them to quit, which they do. After a year (with demonstrated compliance to their group), you then look for an association between lung cancer and level of smoking.
(B) To see how observant your friends are, you part your hair on the left side one month and then switch the part to the right side the next month. You keep track of who notices the change.
(C) To figure out how to make the ideal elk steak for your guests, you compare the recipes of different chefs whose steaks you have tasted in the past. You choose the recipe that is simplest but whose steak also met your standards of excellence.
(D) Your mechanic replaces the spark plugs and spark plug wires in your car, and your mileage improves. You then change the spark plugs in your car back to the old set to see if the improved mileage is due to the new plug wires.
(E) You are in charge of a small airport in which two skydiving deaths have occurred in the past 3 years. You institute a mandatory checklist for all skydivers to complete before takeoff to see if the accident rate declines.
(F) In an effort to identify the causes of university student academic success, a researcher monitors the habits of university students and matches those habits to GPA.
Random
20. (6 pts) You do a statistical test of the difference between the average values observed in a treatment group and a control group. Which of the following options about P-values are true? MTF
A) The P-value is the probability that the difference between the averages (of the treatment and control group) is due to something other than randomness (or, in other words, due to something other than sampling error).
B) A result of P< 0.95 is considered the minimal threshold for accepting the model that treatment and control group averages are not due to just randomness (sampling error).
C) A P-value less than zero indicates that the null model is true.
D) Two studies with the same difference in averages (between the treatment and control group) will have the same P-value.
E) P < 0.01 means that the null model of randomness would be expected to account for the observed results less than 1% of the time.